Urban Planning & Architecture
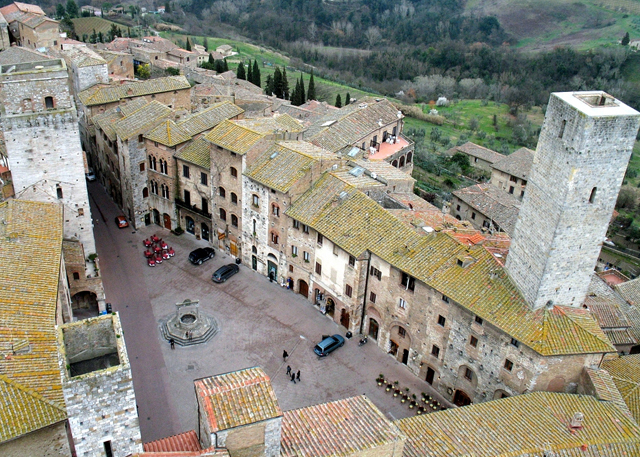

Urban Planning
We can design urban spaces according to ecological and sustainable criteria where each new component is assessed in accordance with its historical and architectural context. This is an essential component of modern planning, as urban design naturally has an impact on social cohesion processes and on the fundamental rules of development which dictate the future shape of a city as it changes in response to changes in the ways of life. Today, more and more often peoples’ lives take place in the networks between cities, the communication webs that allow us to smoothly move from apparently distant places in less time due to the active integration of several related disciplines such as architecture, engineering, ecological science, geography, sociology, law and economics. This is Urbanism: planning and designing past, present and future scenarios that, in addition to dealing with policies, and technical and legislative regulations, aims to improve urban quality and the lives of its inhabitants.
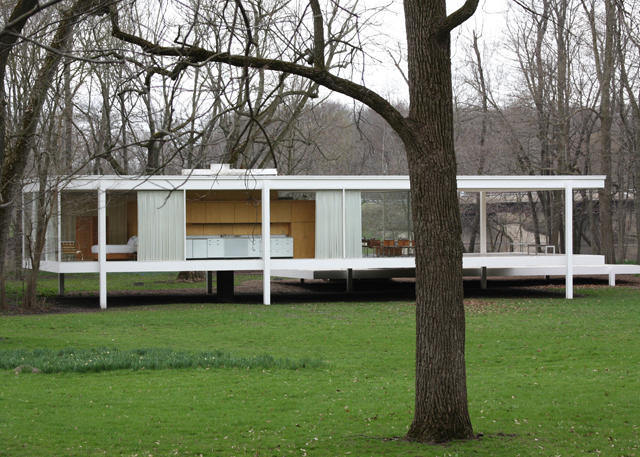

Architectural design
«Constructive clarity brought to its exact expression. This is what I call Architecture» Mies van der Rohe, 1925. «The architect should be equipped with knowledge of many branches of study and varied kinds of learning, for it is by his judgement that all work done by the other arts is put to test. This knowledge is the child of practice and theory» Vitruvio, De Architectura, 15 B.C. Architecture is the result of this multidisciplinary approach, oriented to simultaneously fulfill the three fundamental requirements that animate it: structural, functional and aesthetic, and not necessarily in that order. In different times and in different epochs, history suggests that the same approach should be taken:
- Generate a preliminary design, which is obtained with sketches and notes to describe the work in relation to the various assumptions and constraints applying to the context, and deriving from the needs of the client and from aesthetic considerations;
- Create a definitive design, consisting of graphics and reports to fully understand the work in all of its parts;
- Produce Executive plans, complete with all the essential elements of the construction, from general to particular.
Structural Design
Choosing the type of structure to be implemented in relation to the materials to be used – wood, stone, steel, concrete – and the various constructive techniques deployed on the basis of an accurate and meticulous design. This entails compatibility analysis with the existing materials in the case of consolidation for optimum structural interventions in terms of durability. Knowledge of the future maintenance costs and a high level of security are essential.. Particular attention must be paid to the stress analysis of every element used irrespective of whether the buildings involved are to be consolidated or are new structures. Higher quality standards will be obtained from a continuous dialogue between the realities of the surrounding territory and physical context, with the requirements of the architectural design involved, with the different systems requirements of the project, and, ultimately, with the life and human activities that will actually be carried out within the installation.
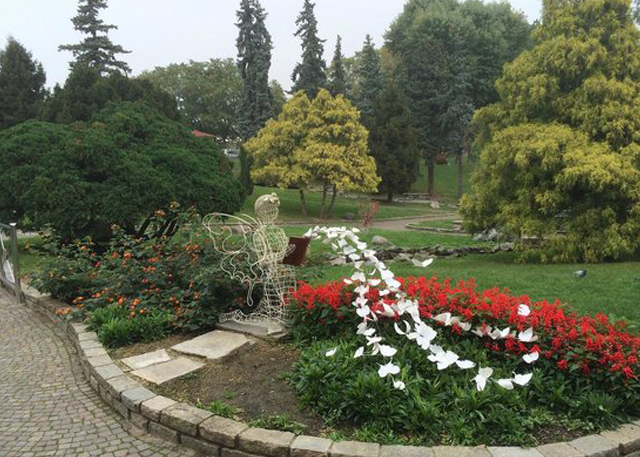

Landscaping
Admiration for the Italian countryside is a general sentiment felt world-wide. That image evokes to the ability of human intervention to create admirable environments. Innumerable gardens and parks have been created throughout Italy during its millennial history and have served as as a beacon of design and as a benchmark for European tradition. This cultural heritage stimulates and underpins the contemporary urge for green design that now has an international and contemporary character. Design of gardens and urban parks in harmony with the natural and the human dimension, that are economically and environmentally sustainable characterizes the place where we design and our technical capabilities and design ethos.
